Error Handling in PHP - part-1
What is Error Handling?
Errors are common when dealing with programming languages. Everyone have experience with errors when writing programs. Errors may occur due to several reasons. Sometimes there will be codes with syntax errors or there will be an unexpected conditions during the execution of your program. You can identify syntax errors at the compile time. suppose that you have to read an XML file or write text file to a folder. At the run time, the file or directory might not be exists. So your program encountered with an error. But you can mange this by check file/folder existence before read/write it. Likewise there are program techniques and in-built methods to handle program errors. This tutorial will explain you error handling configurations in PHP.
Why we need to handle programming errors?
Errors may not only cause to stop your program execution but also give chances to hackers to destroy your system. When program stops with an error, it shows the reason for the error and print a stack trace (this will depend on your php configuration). This will open a back door to the system and there can be a great security risk. Errors leads to providing an attacker with more information that he can use to break your system. So if you forget to handle errors, any one can see the error and the reason for the error. This may cause to reveal your internal file structure to a third party. This is a dangerous case. So error handling is very important in every programming language.
Advantages of handling errors
You can simply off the error reporting using PHP configuration file. (php.ini). But it is not a good idea. Because user get confused. Because there is no clear explanation about the error. So user will be lost. He don't know what has happened. So at least you have to say "An unexpected error has occurred" to the user. So user will know there is a critical error and difficult to continue the program execution. As a programmer you can write a log file with the error details and create bug reports for analyze the problem later. Error handling makes your system more secure. Because no one see the actual error message or internal file paths.
How to write error free code?
We can catch an identify most of the programming errors. Errors break the normal flow of the program execution. This may happen due to following reasons.
- Usage of uninitialized variables.
- divided by zero.
- Invalid function arguments or user inputs.
- NULL references.
- Endless loops / recursive functions.
- Program meets an un expected condition.
- Unavailability of file, database, or network resource.
- Disk faults and network errors.
Error handling settings in PHP
PHP has good error reporting mechanism for error handling and logging. Error reporting controlled via php configuration file (php.ini). You can see the php configuration file in your PHP installation folder. By default PHP comes with two configuration files.
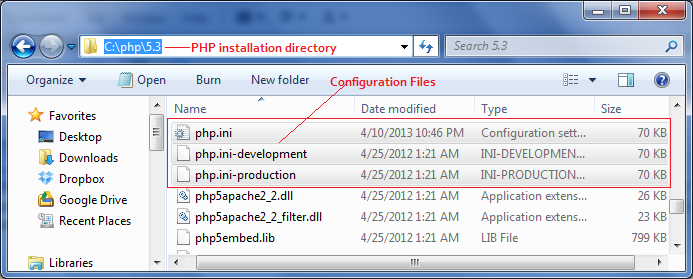
You
can see there are two configuration files named "php.ini-development" and "php.ini-production". Before you upload your code to live server you have to test it locally. So use "php.ini-development" file in your local development environment. Because it contains settings recommended for use in development environments. php.ini-production file contains settings recommended for use in production servers.
When you configure php with apache web server, rename one of the above files to php.ini (this depends on your requirement). Before you do modifications to the original configuration files it is wise idea to keep a copy of that file with you.
Security is very important in production servers. So
"php.ini-production" file contains security and performance settings. It never shows errors to the application users. But in development version it shows all errors. Because it helps developers to identify issues in the program. For an example you can use a variable without initializing before you use it. Under development settings it will show you a notice regarding the undefined variable. But under the production environment it does not show any warning.
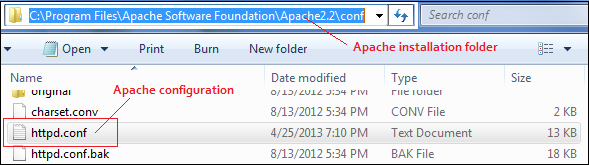
When PHP starts up it reads the php.ini file This happens every time when you starts the web server. If you use apache web server, you can specify where the php configuration file
is located. To do this open the apache installation folder and search for httpd.conf file. In windows system by default it is located in "C:\Program Files\Apache Software Foundation\Apache2.2\conf" directory.
Use PHPIniDir variable in apache configuration file to specify the php.ini file. it tells the apache to the where to search for php.ini file. By default PHP search C:\Windows directory for the php.ini file.
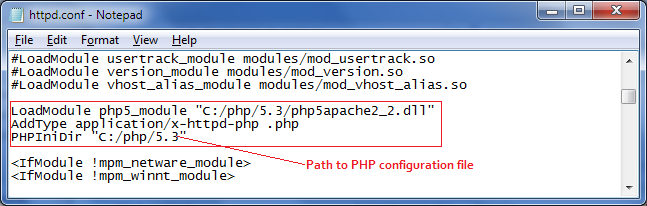
Also you can set custom php configuration files in each directory. Then it overrides default configuration settings according to the new file. But this will make your system more complex. because you have to refer all configuration files when fixing bugs. In shared hosting environments you can't override all settings in the parent php.ini file by using your custom file. There are some limitations. Also you can change some settings at the runtime. That means you can specify php.ini directives in your code. You can use string ini_get ( string $varname ) to view the current setting and string ini_set ( string $varname , string $newvalue ) to set new values at the runtime. Also you can set these values in .htaccess file. You can set all error reporting
directives at the run time.
PHP configurations settings for handling errors
You can see there are list of settings that are related to error reporting in php; under the "Error handling and logging" section of the php.ini file. That directive informs PHP to which errors should be displayed and which are not. Error reporting is a process that consume server resources. Because it increase the I/O activity when logging every error to the log file.

In PHP there are number of Error Level Constants that use to report errors. You can customize those settings. By default error_reporting is set to E_ALL | E_STRICT. This means it displays all errors and notices. You can set this option in your development server. Errors are classified to several groups. Basically there are
- Errors - about Fatal runtime errors- It stops the program execution
- Warnings -about run time warnings/ non fatal errors - Can continue script in to some extend
- Notices - about run time notices - can continue program execution.
- Deprecated - about code that will not work in future versions.
Also you can use combination of above constants with bitwise operators ('|', '~', '!', '^' and '&'). ~ is use to exclude a error level and | is use to include error level.
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE (Show all errors, except for notices and coding standards warnings.)
If you need to show errors only you can set,
error_reporting = E_COMPILE_ERROR|E_RECOVERABLE_ERROR|E_ERROR|E_CORE_ERROR
Likewise you can set custom error_reporting values.
Display Errors in PHP
You can set display errors ON or OFF. This section divide into two sections program errors and startup errors. Startup errors are errors that occur during PHP's startup process. For a example fail to load specific library cause such kind of error. If you off display errors, no errors will be displayed even there are fatal errors. By default this directive set to On in development environments while it set to Off in production environments. This only stops displaying errors to the user. But errors are logged in the error log. You can see errors by opening the error log.
display_errors = On (Show all errors which are specified in error_reporting directive)
display_errors = Off (Prevent displaying errors to the user)
display_startup_errors = On (show errors which occur during PHP's startup)
display_startup_errors = Off (hide PHP's startup errors)
Logging Errors in PHP
PHP can log errors to a server specific log. By default all errors are send to the apache error log. Log errors is very important. Because in production environment no other way to track errors. Also you can specify a error log. Using apache Virtual Hosts you can set custom error logs for each domain. This make error tracking easy. Otherwise all errors sent to one log file and difficult to filter errors. By setting custom error files you can quickly find errors related to the host. Also you can set the maximum error log file size.
Sometimes you may experienced with repeated error messages. Suppose that you have forget to pass a function argument in a loop. This will cause to repeat the same error for several times. With PHP error logging settings, you can ignore repeated errors. If you enable this setting no repeated errors will be displayed.

log_errors = On (Log errors to the error log file)
log_errors = Off (Disable the error log)
log_errors_max_len = 1024 (set the maximum error log file size)
log_errors_max_len = 0 (maximum error log file size not applied)
ignore_repeated_errors = Off (No repeated errors will be logged in the same file)
gnore_repeated_errors = On (Repeated errors will be logged)
ignore_repeated_source= On (If the same error occurred in different files ignore repeated source)
ignore_repeated_source= Off (Display same the same error if they appear in different files)
report_memleaks = On (Memory leaks will be logged. This has only effect in a debug compile)
report_memleaks = Off (Memory leaks will not be logged)
track_errors = On (Store the last error/warning message in $php_errormsg)
track_errors = Off (No errors.warnings will be stored in $php_errormsg)
How to log errors to a custom file in PHP?
By default all PHP errors are send to Apache error log. You can change this and set to a custom file. Also you can send PHP errors to system event log.
error_log = my_php_error.log (Log errors to your custom file)
error_log = syslog (Log errors to system event log)
You can this directive empty to send errors to Apache error log (Default PHP behavior).
PHP Error display settings
You can control error display settings in PHP. Basically PHP displays errors as HTML out put and with links to php documentation related to that error. It is easy to understand the error. However this feature is recommended to disable on live production servers due to security and performance reasons. But it is easy to use local documentation in your development server. because you can easily access to the documentation Also no internet access required.
You can format error messages using some CSS formatting. PHP allows you to append HTML elements to the beginning of an error and the ending of an error message. See bellow configuration to setup local PHP documentation.
html_errors = On (Inserting HTML links to documentation related to that error)
html_errors = Off (No documentation links)
docref_root = "http://localhost/phpmanual/" (Your local copy of PHP documentation)
docref_ext = .html (Hide PHP's startup errors)
error_prepend_string = "<span style='color: #ff0000'>" (String to output before an error message)
error_append_string = "</span>" (String to output after an error message)
Note: you can add span or div tags for prepend and append strings and use CSS to change the styles.


3 comments:
phí ship hàng từ mỹ
giá ship hàng từ mỹ
ship hàng us
đồ usa
ship hàng mỹ về việt nam
This is an awesome post. Really very informative and creative contents. This concept is a good way to enhance knowledge.
learn MSBI course
MSBI online training course
MSBI training course
1xbet korean - Bet online, live and live in-play for real
1Xbet 1xbet mobi is a new sports betting website that aims to revolutionise the world of sports betting in South Korea with a focus on football.
Post a Comment